
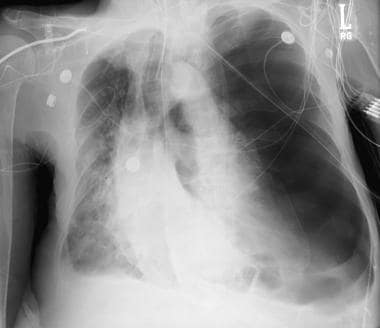
The use of mechanical ventilation in acute asthma is closely associated with some life-threatening complications such as pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum and subcutaneous emphysema. Pulmonary interstitial emphysema, status asthmaticus, barotrauma, mechanical ventilation INTRODUCTION Minimally invasive management by percutaneous trans-thoracic intrabullous chest-tube drainage is feasible, safe and relatively effective.The present case highlights the importance of crash induction, cautious airway management and protective re-ventilation in the management of acute respiratory failure with dynamic hyperinflation, such as status asthmaticus.We describe ventilation-induced tension pulmonary interstitial emphysema combined with contralateral pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum and subcutaneous emphysema which developed immediately after difficult airway management of acutely decompensated asthma in an adult.The treatment of our patient is described.

Patient: We describe the case of a 64-year-old man who presented with huge pulmonary interstitial emphysema together with simultaneous pulmonary barotrauma in status asthmaticus requiring invasive ventilation.ĭiscussion: There are no guidelines for the management of such complications and their possible sequelae but conservative treatment seems to be effective. Management and clinical sequelae are poorly described. Described more frequently in ventilated new-borns, pulmonary interstitial emphysema is an uncommon barotrauma-related complication in adults. Introduction: Pulmonary interstitial emphysema is a rare finding defined as abnormal air collection inside the lung interstitial tissues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
